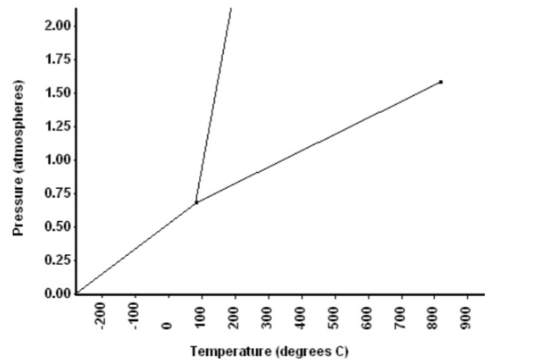
Refer to the phase diagram below when answering the questions on this worksheet. Begin by adding S, L, and G to the three regions of the phase diagram. 2.00 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 Temperature (degrees C) 1) What is the normal freezing point of this substance?_100 °C 2) What is the normal boiling point of this substance?_350 °C 3) What is the normal boiling point of water? 100 °C 4) What is the normal freezing point of water? °C If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of 300°C and then lowered the pressure to 0.25 atm isothermally (constant T), what phase transition(s) would occur? 5) Liquid to gas transition would occur 6) At what temperature do the gas and liquid phases become indistinguishable from each other? 800 °C What is this point called? If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 0.75 atm and a temperature of -100° C, 7) what phase change(s) would occur if I increased the temperature to 600° C? At what temperature(s) would they occur? 001 007- (sə Jəydsoune) ənssəd
Refer to the phase diagram below when answering the questions on this worksheet. Begin by adding S, L, and G to the three regions of the phase diagram. 2.00 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 Temperature (degrees C) 1) What is the normal freezing point of this substance?_100 °C 2) What is the normal boiling point of this substance?_350 °C 3) What is the normal boiling point of water? 100 °C 4) What is the normal freezing point of water? °C If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of 300°C and then lowered the pressure to 0.25 atm isothermally (constant T), what phase transition(s) would occur? 5) Liquid to gas transition would occur 6) At what temperature do the gas and liquid phases become indistinguishable from each other? 800 °C What is this point called? If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 0.75 atm and a temperature of -100° C, 7) what phase change(s) would occur if I increased the temperature to 600° C? At what temperature(s) would they occur? 001 007- (sə Jəydsoune) ənssəd
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter11: Intermolecular Forces And Liquids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 33GQ
Related questions
Question
Need answers for blue parts

Transcribed Image Text:Refer to the phase diagram below when answering the questions on this worksheet. Begin by adding
S, L, and G to the three regions of the phase diagram.
2.00
1.75
1.50
1.25
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0.00
Temperature (degrees C)
1)
What is the normal freezing point of this substance?_100
°C
2)
What is the normal boiling point of this substance?_350
°C
3)
What is the normal boiling point of water? 100
°C
4)
What is the normal freezing point of water?
°C
If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 1.25 atm and a temperature of 300°C and
then lowered the pressure to 0.25 atm isothermally (constant T), what phase transition(s)
would occur?
5)
Liquid to gas transition would occur
6)
At what temperature do the gas and liquid phases become indistinguishable from each other?
800
°C
What is this point called?
If I had a quantity of this substance at a pressure of 0.75 atm and a temperature of -100° C,
what phase change(s) would occur if I increased the temperature to 600° C? At what
temperature(s) would they occur?
7)
Pressure (atmospheres)
00L
Expert Solution
Step 1
The phase diagram given is,
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
